FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE
Media Contact:
Tara DiMilia, 908-947-0500, tara.dimilia@TMstrat.com
Bay Area Lyme Foundation Selects National Winners of the 2021 Emerging Leader Awards to Advance Research for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Lyme Disease
Brandon Jutras, PhD of Virginia Tech, Nitya Ramadoss, PhD of Stanford University and Michael P. Rout, PhD of The Rockefeller University are this year’s recipients
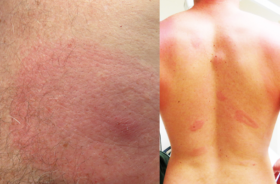
PORTOLA VALLEY, Calif., July 6th, 2021—Bay Area Lyme Foundation, a leading sponsor of Lyme disease research in the U.S., announces the recipients of the 2021 Emerging Leader Awards (ELA), which are designed to support promising scientists who represent the future of Lyme disease research leadership. Michael P. Rout, PhD of The Rockefeller University will receive $250,000 for his work with nanobodies to develop a sensitive point-of-care diagnostic. Brandon Jutras, PhD of Virginia Tech and Nitya Ramadoss, PhD of Stanford University will each receive $100,000 toward the development of a novel direct-detection diagnostic approach for Lyme disease and a novel therapeutic based on B-cell mapping, respectively. Lyme disease is a potentially disabling infection diagnosed in nearly half a million Americans each year.
“As there is not a diagnosis or treatment that works for all patients, there is a critical need to develop direct-detection diagnostics as well as treatments that can prevent the development of persistent Lyme disease, and we are excited to support these novel approaches that have shown success in other areas,” said Linda Giampa, executive director, Bay Area Lyme Foundation.
Two of the award winners will utilize biological samples from the Lyme Disease Biobank, a program of the Bay Area Lyme Foundation, to collect well-characterized human tissue, blood and urine specimens to accelerate research of Lyme disease and other tick-borne infections.